Describe the Following Cell Surface Modification Using the Table
In nature plasmids often carry genes that. Using T cell trogocytosis 10 or reporter genes 11121314 a suite of technologies have been developed in this area enabling high-throughput screening for T cell antigens such as SABR 11 MCR.
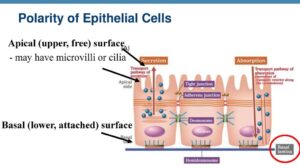
Epithelial Polarity Apical Basal Lateral Surfaces Of Epithelial Cells Science Online
Table 1 shows the minimum volume necessary for varying concentrations of ligand given a receptor number of 10 10 10 5 cells 10 5 receptorscell a standard estimate when testing proteins expressed on the yeast cell surface Boder Wittrup 2000 or mammalian cell surface discussed in Sections 4 and 5 respectively.

. Lipidation markedly increases the hydrophobicity of proteins resulting in changes to their conformation stability membrane association localization trafficking and binding affinity to their co-factors. To mimic single-cell proteomics preparation in nanowell chips 01 ng peptide samples in 200 nL buffer from the three cell lines were loaded into 12 mm nanowells using a nanoPOTS dispensing robot. A plasmid is a small extrachromosomal DNA molecule within a cell that is physically separated from chromosomal DNA and can replicate independently.
They are most commonly found as small circular double-stranded DNA molecules in bacteria. Protein lipidation is an important co- or post-translational modification in which lipid moieties are covalently attached to proteins. However plasmids are sometimes present in archaea and eukaryotic organisms.
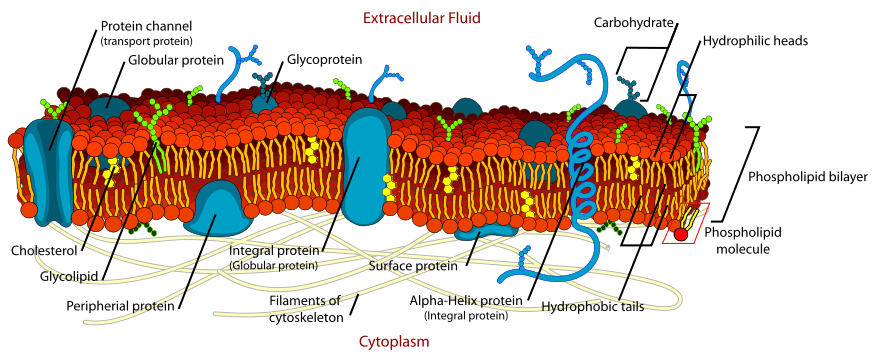
The Cell Membrane Structure Phospholipids Teachmephysiology
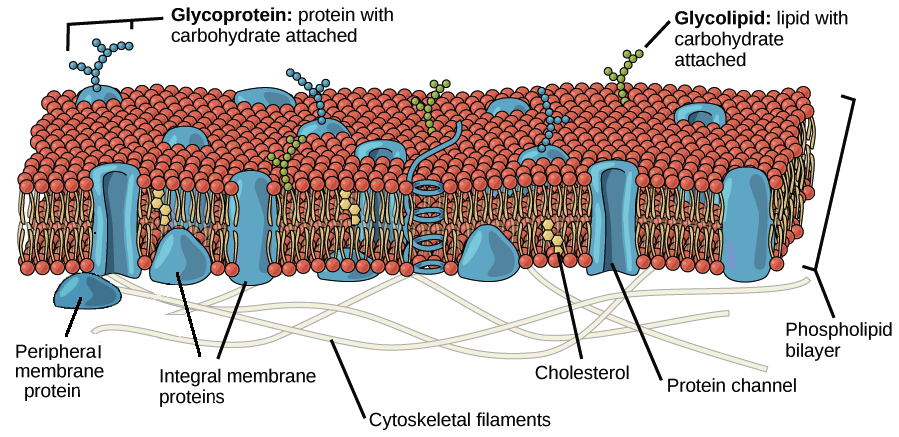

No comments for "Describe the Following Cell Surface Modification Using the Table"
Post a Comment